2024/9/12 14:24:06
Resources
Pressure drop problem and effective energy saving of air compressor system
Pressure drop is the pressure drop, in the compressed air system refers to the air pressure reduction from the air compressor exhaust port to the actual gas point, under normal circumstances, the exhaust pressure increases by 1 kg, the total flow of the air compressor energy consumption will increase by 7%-12%, so how to minimize the pressure drop is an important part of the energy-saving transformation of the compressed air system.
What is pressure drop:
pressure drop (pressure drop) refers to the pressure drop caused by energy loss when the fluid flows in the pipeline. The fluid in the compressed air system is air, of course, if the compressed medium is other process gases are also applicable.
Compressed air pressure drop refers to the pressure reduction from the compressor exhaust port to the actual gas point, also known as pressure loss, pressure difference, etc. Pressure drops occur when compressed air passes through post-treatment (such as dryers, storage tanks, filters, etc.) and distribution systems (such as pipes, valves, etc.).
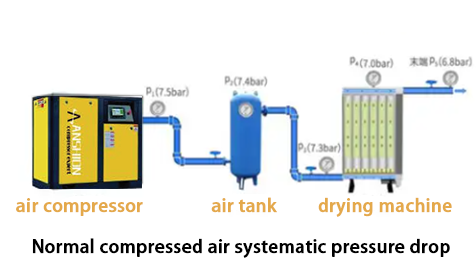
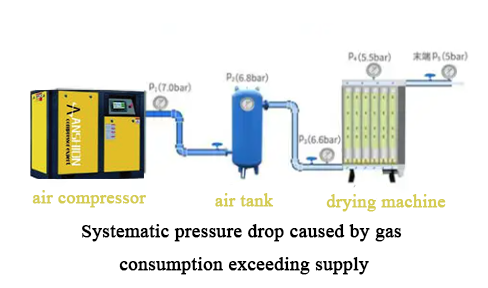
The pressure drop of the compressed air system is usually composed of the pressure drop caused by the resistance of the pipeline system itself and the pressure drop caused by the shortage of gas supply due to the increase of gas consumption, which is called the systematic pressure drop. Because people tend to focus on the former, they ignore that most of the pressure drop in compressed air is caused by systematic pressure drop.
Causes of pressure drop:
When the gas consumption at the end of the compressed air is matched with the rated output flow of the air compressor, the pressure drop of the system is low, and if the gas consumption at the end is too large, exceeding the rated output flow of the air compressor, the pressure drop of the entire system is relatively large. Any type of blockage or restriction in a compressed air system will cause airflow resistance and create a pressure drop, which is theoretically unavoidable. The most direct cause of air pressure loss is the resistance formed by the friction between compressed air and the inner wall of the pipe. The larger the diameter of the pipe, the more air gathered in the center of the pipe, the smaller the friction resistance in the pipe. Conversely, the greater the resistance, the greater the pressure drop.
The pressure drop is not entirely due to the friction resistance of the pipeline system, but the greater reason is the systematic pressure drop. Because the adsorption cylinder of the adsorption dryer is a small container, its pressure will directly reflect the pipeline pressure near the end, and the front section of the adsorption dryer will keep close to the exhaust pressure of the front-end air compressor due to the limitation of the pipe diameter, so there will be a very large pressure difference at the inlet and outlet of the adsorption dryer, which is often mistaken for the equipment itself, which is not correct. Therefore, it is scientific and accurate to judge that the pressure drop of the adsorption dryer itself can only be measured under standard working conditions.
The harm of excessive pressure drop:
The industry generally believes that within the range of 0.7MPa, the exhaust pressure increases by 1 kg, and the energy consumption at full flow will increase by about 7%. But in fact, higher pressure than needed also creates more wasted energy. For example, increasing the compressor exhaust pressure will increase additional gas losses for various uncontrolled uses, including leaks, blowdowns, etc. After the above energy waste is included, the total energy consumption increase can soar to about 12% for every 1kg increase in system pressure. Therefore, minimizing the difference in air pressure between all the components of the system is an ideal state that we are constantly striving for.
How to deal with the pressure drop problem:
In compressed air system, pressure drop is one of the factors that consume enterprise energy and cost. If the system pressure drops below the working pressure required for pneumatic tools and automation equipment, the process production efficiency will drop sharply, resulting in huge cost losses for enterprises. The significant cause of the system pressure loss is that the compressor exhaust is too small, and the supply can not meet the demand of the air consumption. In addition, too many pneumatic tools and automation equipment that need to use compressed air, or too many leaks in the distribution gas pipeline, will also cause pressure loss in the system. The hidden reason for the air pressure loss is that the compressed air is caused by the friction resistance of the inner wall of the distribution gas pipe. The larger the diameter of the trachea, the more air will be concentrated in the center of the trachea, and the smaller the friction resistance in the tube. The compressed air pressure drop or pressure loss also depends on such factors as gas volume matching, initial pressure, pipe type, pipe length, number of valves, joints and bends in the system, etc. Therefore, it is very important to reasonably select air compressors, gas quality equipment (commonly known as: post-processing equipment), gas distribution pipelines, etc., and to have an appropriate amount of system redundancy to avoid unreasonable systematic pressure drops.